Award-winning and Fully Accredited
Thousands of graduates worldwide take advantage of our virtual online programs. Many of our most successful graduates are from around the world, including the United States, Latin America, Southeast Asia, and the Middle East.
Our certificate pathways connect state, industry, and national standards with real-world skills to prepare students for career success and further education. Our accredited school’s official transcripts and certificates are issued upon completing the online program.
Our Career Technical Education Priorities
Our catalog prioritizes offering complete CTE programs of study in high-pay, high-demand career clusters. Carefully designed sequences of introductory, intermediate, and capstone-level courses ensure students graduate ready for a job, certification, or technical school. Built to state, industry, and national standards, our Lena Certificate Courses provide students with the knowledge and skills required for career readiness.
A Student-Centered Learning Experience
Each lesson includes multiple opportunities for students to build knowledge through inquiry, creation, connection, observation, and confirmation. This active learning approach develops critical thinking skills and prepares students for success in the workforce.
As students move through the CTE courses online, they benefit from continual feedback, opt-in support, and scaffolds embedded in the courses. Schools may offer courses as whole-class instruction or as asynchronous learning.
Accounting I
In the Accounting I Jump Course for high school, students will learn a basic overview of the different functions in accounting. This includes rules for financial reporting and the parts of the balance sheet, income statement, and statement of stockholders’ equity and retained earnings. Students will then be guided through the accounting cycle, learning how to create these documents and utilize them within a corporation. Students will journalize payments and invoices in accounts payable and accounts receivable, understand the different methods of inventory, and calculate payroll and taxes. Students will complete the course with the Accountant Simulation Project, an assignment where they will fulfil all steps of the accounting cycle without guidance and then present a completed cycle with notes for future opportunities for their simulated corporations.
Advertising
The Advertising course teaches the principles and practices of advertising as an integral part of marketing communication. The course begins with a look at the professional opportunities available in the advertising field. Students are asked to consider environmental, ethical, and other professional responsibilities. They learn about the marketing research process and the components of advertising using the PESO model. Students apply demographics, segmentation, and the four major sales channels to define target markets and make a sales presentation. In the final Module, students use the knowledge gained about the product cycle to complete a final project simulating a promotional campaign for a new product.
Audio/Video Production
Audio/Video Production I explores foundational principles in both audio design and video production. This course is broken down into four primary sections: preproduction, principal photography, postproduction, and career preparation/portfolio development. Each section focuses on the primary elements found in each phase of production. Preproduction explores topics, such as script and storyboard development, production documents, and production planning. Principal photography analyzes key crew roles associated with audio and video production, like the director, sound designer, producer, and actors, as well as shooting techniques, camera gear, and on-set safety. Postproduction delves into topics, such as video editing, copyright laws, and sound mixing and design. The course concludes by having the student create an audio/video portfolio, resumé, and cover letter to prepare for entry into college and the professional world..
Business Management
Business Management is an integral part of the Business, Marketing, and Finance Career and Technical Education clusters. Students will examine evolving views of management with an emphasis on leadership. Next, students will consider ethical case studies and analyze the strengths and weaknesses of various organizational structures. In units 4 through 6, students will analyze the decision-making process as it applies to management issues, such as quality control and improving communication. Beginning with unit 7, students will investigate employee compensation and legal matters concerning hiring and firing. The course concludes with a presentation of practical tools to build one’s personal habits and to nurture team building.
Career Prep
In Career Prep, students are given tools to be successful in future careers. The career clusters and their associated career paths are the focus of the course. Students will learn how to survey the job market, fill out paperwork, and thrive in the workplace. Students will create an electronic portfolio throughout the course. The portfolio includes letters of interest to employers, resumés and cover letters, interview preparation documents, a career plan, as well as other reports. The course is designed for students who are currently working and can leverage real-life experience into their course projects.
Child Development
Child Development prepares students to understand the physical, social, emotional, and intellectual growth and development of children. The course is designed to help young people acquire knowledge and skills essential to the care and guidance of children as a parent or caregiver. Emphasis is on helping students create an environment for children that will promote optimum development. Students also investigate careers in child development.
College and Career Transitions
This course is designed to equip students with the knowledge, skills, and abilities necessary to be active and successful learners, both in high school and in college. Students examine numerous research-based learning strategies that are proven to lead to academic success such as goal setting, effective time management, handling stress, note-taking, active reading, test-taking strategies, and conducting research. In the College and Career Transitions course, students will research financial scholarships and grant opportunities, complete applications, and explore technical schools, colleges, and universities. With the increased emphasis on career and college readiness and post-secondary education, students need a course that will provide opportunities to meet these post-secondary opportunities in grades 9–12.
Counseling and Mental Health
This course is a Career and Technical Education course for use in the Health Science or Human Services career pathways. The course covers general topics for personal and professional development (soft skills), such as time management, critical thinking, and problem-solving, communication, team building, ethics, and character. It also focuses on many mental health topics, including the history of mental health care, modern mental health care systems, the nervous system, mental health across life stages, stress, depression, and other mental disorders. Students research the professional development of workers in the mental health field, such as the scope of practice, ways to recognize abuse, and methods for adapting to change. Student and professional organizations for career development are discussed as well. The course ends with activities exploring careers and researching training opportunities.
Entrepreneurship
The Entrepreneurship course is designed to grow the student’s passion for starting, growing, and excelling in business ventures. The student will explore the basics of starting a business, from brainstorming great concepts to execution and profitability. Entrepreneurship includes more than just starting businesses, but explores the ventures of product development, marketing, distribution, and sales. The student will expand his or her knowledge in the areas of proper product and service pricing, financial planning and growth, accounting and bookkeeping, fundraising, marketing research, and business law. The course asks the student to practice the knowledge and skills he or she has gained by developing and writing a business plan for their very own business venture. The student will gain a complete understanding of what it takes to make a business a success and possibly gain a desire to actually start a company from scratch.
Human Resource Management
Human Resources Management (HRM) is vital to every organization. In this course, students will discover the role of the human resource manager. They will define the role, as well as policies, procedures, and legal requirements within the role. Students will also cover the life cycle of the employee, including hiring practices, training, labor laws, discipline, reward, benefits, and termination. Stude nts will discover how to be human resource professionals are liaisons for both the organization and the employees. Students will learn how to enforce employer responsibilities while protecting employee rights. Through a better understanding of human resource management, students will learn how to become better managers and employees in the future.
Investigating Careers
In this course, students are introduced to various aspects of the workplace and are given guidance in career preparation. This includes guidance toward becoming work-ready, for job acquisition skills, for continued training for job advancement, and for work-life balance. Topics include self-evaluation for career choice, the labor market, personal and professional development, getting a first job, personal characteristics for work, and making decisions. The importance of teamwork and leadership are a main emphasis in the course. The course includes instruction on using online tools to review and assess interest in various careers.
Medical Microbiology
Medical Microbiology explores the world of tiny (micro) organisms that are responsible for making people sick. Students learn about the common bacteria, viruses, and protists that cause sickness and disease in humans. Medical Microbiology delves into different ways these germs and diseases can spread from person to person, throughout a community, and eventually around the globe while discussing the best practices for stopping them from spreading. Students look into different medications and how they work to kill or slow the growth of different microorganisms. Students will also research why some antibiotic medications are no longer effective against the bacteria that cause disease. Medical microbiology also teaches laboratory skills in how to effectively grow and isolate different colonies of microorganisms in Petri dishes.
Wearable Technology Innovations
From hearing aids to pedometers to smart watches, humans have made and worn devices to overcome physical deficiencies, count their steps, and communicate. With the continue miniaturization of chips and sensors, combined with increasing sophistication of artificial intelligence, wearable technology has proliferated into countless end-markets. This course will introduce students to wearable technologies and the components and software that make these technologies possible. The course will also evaluate several applications of wearable technologies in various industries. Finally, the course will examine and discuss the implications of wearable technology, including its pros and cons, and potential implications to our health, privacy, and society.
Transportation Technologies
This course introduces students to the newest and most cutting edge futuristic transportation technologies out there. Students gain familiarity with the history of transportation development and understand a framework with which to evaluate new transportation modes. Then the course dives into 10 different technologies on the horizon. Students examine the technologies, the pros and cons of each mode, and explore potential career paths in these emerging fields.
The History of Gaming and Esports
In this course, students will learn about the technologies and design principles that have been the foundation of the development of video game technology over the last 50 years. Students will examine and discuss the impact of video games on culture and the economy. Students will learn about the current gaming and e-sports landscape, including strategies and techniques of top teams and individuals. This course will also discuss the risks and dangers of video games and understand how to set appropriate time and content parameters. Finally, the course will identify career paths and opportunities for those who are passionate about gaming.
Startups and Innovation
Students hear a lot of contradictory advice in life. On one hand, they may hear something like “Follow your dreams. Pursue your passion and the money will come!” On the other hand, they may hear something completely opposite, like “Most startups fail! It’s much safer to get a safe, steady job.” So which side is right? Given the massive changes to the economy and society, the skills of entrepreneurship are going to be critical in building a lasting career. The entrepreneurial mindset of searching for opportunities, creating value, and solving pain points will always be valuable. And this mindset applies not just to starting a business, but in any organization that someone is a part of: school, established companies, or non-profits. In this course, students will explore how to use this mindset to create the next world-class startup.
Smart Cities
This course will provide students with an overview of smart cities. The course will begin by providing a foundational explanation of what constitutes a smart city and why they are beginning to pop up around the globe. With a firm understanding of what a smart city is, the majority of the course will focus on various aspects of them such as energy, transportation, data, infrastructure, mobility, and Internet of Things devices. The course will conclude with an analysis of careers related to smart cities.
Medical Terminology
Medical Terminology is a course for students with an interest in the medical field. This course provides students with knowledge of Latin and Greek roots, prefixes, and suffixes in addition to combining forms and eponymous terms related to the many systems of the human body. Students are also able to learn more about the many professions, specialists, and treatment plans associated with different areas of the body. This course introduces new ways of looking at the body through the lens of medical terms and their origins.
Principles of Business, Marketing, and Finance
The Principles of Business, Marketing, and Finance course will expand the student’s knowledge in the many areas of business and free enterprise. The majority of the course takes a comprehensive look at business disciplines such as analyzing goods versus services, economics, financial management, principles of personal finance, marketing, the global economy, and government in business. The student will gain soft skills such as understanding business ethics, leadership, and the management of employees. The student will gain hard skills such as product management, finances, marketing campaigns, and sales. The course then takes a practical look at career opportunities in business and the professional skills needed to excel within the industry. The student will finish the course with a broad grasp on the principles of starting, operating, and managing a successful company.
Principles of Education and Training
Through an examination of the Principles of Education and Training, students will study the roles and responsibilities of teachers, administrators, and administrative support professionals. Students will analyze the characteristics, qualities, and traits of highly successful educators. Students will evaluate a variety of educational options available on their road to becoming professional educators. Students will also study the opportunities and paths possible when becoming corporate trainers or independent contractors, providing training services to a variety of clients. Throughout this course, students will have learned methods of classroom instruction and ways to develop Lesson plans. Students will use critical thinking skills to develop their own personal philosophy of education. Students will learn via the perspectives of students, teachers, and support professionals using real-life examples and situations to explore what it means to be an “educator for life.” Students will end this course by developing a graduation plan that leads to their calling as professional educators.
Principles of Government and Public Admin
Principles of Government and Public Administration (PGPA) introduces students to careers in public policy. PGPA explores government from the perspective of government and private-sector employees as well as elected officials. In this course, students examine different career avenues and their ethical and professional standards. PGPA introduces students to theories of governmental development alongside the constitutional principles underlying America’s federal and unitary forms of government. Students learn about the public official’s responsibility to protect citizens’ rights to due process and discover how interest groups influence public policy. Students then analyze the effect of policymaking on both the culture and society of the nation and foreign policy. The course concludes with an investigation into the role of government in a free-market economy, including its ability to stimulate invention and innovation.
Principles of Human Services
This course enables students to investigate careers in human services including counseling, mental health, early childhood development, family and community, and personal care services. Each student is expected to complete the knowledge and skills essential for success in high-skill, high-wage, or high-demand careers. Skills learned in this course includes: responsible decision-making, setting both short- and long-term goals, and knowing how to react to and handle high stress crisis situations.
Principles of Health Science
This CTE course is designed to help prepare students for a career in the health science field. It covers healthcare systems and the roles of team members within these institutions. The course has many opportunities for students to explore the various careers within the healthcare field. It emphasizes the personal and professional skills required to succeed in this arena, including personal character qualities, teamwork, and leadership. Coverage includes the science of healthcare, including measurement, SI system, anatomy and physiology, and safety practices. It covers topics of healthcare at various life stages, from birth to death. Laws and regulations, best practices, and professional ethics are discussed, as well. Because this course has a careers emphasis, other topics covered include career preparation, the role of student and professional organizations, and the state of the health-care career field.
Sports and Entertainment Marketing
In Sports and Entertainment Marketing, students will explore the foundational elements of marketing as they pertain to the sports and entertainment industries. Students will primarily focus on the sports market, but other entertainment industries are analyzed as well, including music, theater, and television. Sports and Entertainment Marketing will require students to practice targeted marketing and segmentation as they relate to entertainment. Students will engage in several projects, including developing a ticket sales strategy, planning game operations, creating event strategies, and making a sports press kit. Students will investigate the distribution of sports and entertainment media, the fan experience, promotional plans, sponsorships and endorsements, as well as business ethics and sports legislation. By the end of this course, students will have an understanding of the career pathways and opportunities available in the sports and entertainment industries.
Video Game Design
Video Game Design is a course designed to help students develop skills for planning, designing, and completing development of an original video game. These skills include outlining and writing a game story, storyboarding, level and objectives design, game mechanics, and character design. Students are also exposed to development skills, including use of pseudocode, decisions, algorithms, collisions, and other programming functions, as well as graphics, animation, and sound. The student will become familiar with the use of suitable game engines for creating their working video game. The course includes discussion to help the student understand the history of video games, as well as their genres. This includes discussions of game theory to help students understand audience expectations, control, and other aspects of game design. Students will be required to create an original video game and submit it for critique. In addition, students will be involved in playing and critiquing the games of other students, as well as critiquing existing video games. The student will be required to create and understand the purpose of a Game Design Document (GDD), an industry standard..
Virtual Business
The Virtual Business course guides students through the basics of starting, operating, and managing an online company. This course is designed for students interested in starting a virtual business by creating a web presence, conducting online and offline marketing, examining and creating business contracts for online business, and exploring project-management systems. The student will also explore bookkeeping processes, applicable legal company business structures, managing telecommuting employees, maintaining business records, as well as entrepreneurship. Virtual Business also guides the student through potential online career pathways by conducting various personality and career pathway assessments. The student will conclude the course by applying learned skills to create a company, including a business plan, branding the business, and creating a website using common website builder tools.
World Health Research
World Health Research introduces students to the various risk factors people face globally. The course shows how health outcomes in developed nations differ from those in developing nations. The course analyzes these trends, along with the origins of primary care. The course compares different organizations that identify and monitor global health threats. World Health Research allows students to explore specific research methods and design studies to understand world health problems and their impacts. The course also shows students the effects of infectious and chronic diseases across the globe, discussing emerging medical technologies and the response of the healthcare system. This course concludes with an analysis of ethical concerns regarding global health, the importance of clinical trials, and ways to enact global change.
Early Childhood Education I
The Early Childhood Education course is designed to provide an overview of the expectations and roles of the early childhood educator. The course provides details about childhood development, health, nutrition, and guidance strategies to help students understand the exciting and unique opportunities that a career in early childhood education can offer. The course is intended to prepare students for challenges they may face, but to emphasize the rewards of being able to influence the life of a young child. The ability to offer support to children as they learn, and grow is a point that is highlighted throughout each lesson.
Early Childhood Education II
The Early Childhood Education II Course is designed to provide an overview of the professional expectations of being an early childhood educator. Throughout the course, students will learn about what it means to be a professional, including the significance of professional development in any educational role. They will review observational methods and the history of education in the United States, with a focus on early childhood and school-age programs. They will spend a significant portion of the course learning about the importance of Developmentally Appropriate Practice (DAP) and how to implement these strategies. Designing physical, social, and temporal environments will also be a major focus of the course, as will developing relationships with families and communities to strengthen their position and knowledge. Additionally, this course will prepare students for the Child Development Associate (CDA) certification exam.
Entrepreneurship & Small Business
This course prepares students for the Entrepreneurship and Small Business Certification exam. This certification has been designed to test concepts around starting and managing a small business. These topics include entrepreneurship, evaluation of opportunities, preparation to start a business, operation of a business, marketing, and management of finances. Students gain insights and understand real-world applications that will not only allow them to succeed in passing the certification exam, but also in successfully starting, working in, or running a small business.
Fundamentals of Bitcoin & Cryptocurrency
Upon completion of this course, students will understand bitcoin, including its history, development, and context within the modern global economy. Students will learn the basic cryptographic principles that underlie bitcoin, and gain confidence by demonstrating strong security principles in storing and transaction bitcoin. Key principles such as mining, wallets, and hashing will be introduced. And finally they will be familiarized with the nascent industry of digital currencies and how they function.
Fundamentals to Blockchain & Cryptography
Blockchain seems to be the latest buzzword that the business world is talking about. But what is it? And why should a high school student care? This course will seek to answer those questions. It will strip away the layers of complexity and sophistication to help students understand the key concepts of the blockchain. The course will introduce and discuss areas where blockchain has the greatest potential.
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
This course teaches what every student should know about Artificial Intelligence. AI is a fast-moving technology with impacts and implications for both our individual lives and society as a whole. In this course, students will get a basic introduction to the building blocks and components of artificial intelligence, learning about concepts like algorithms, machine learning, and neural networks. Students will also explore how AI is already being used, and evaluate problem areas of AI, such as bias. The course also contains a balanced look at AI’s impact on existing jobs, as well as its potential to create new and exciting career fields in the future. Students will leave the course with a solid understanding of what AI is, how it works, areas of caution, and what they can do with the technology.
Introduction to Education & Teaching
This course is designed to prepare future educators for the classroom they will inherit! It starts with a history of education and how blended, adaptive, and personalized learning are coming to the forefront in learning. It then explores new and emerging technologies, along with their current and future impact on education. Throughout the course, students will explore a wide range of career possibilities in the education field and evaluate both the promises and pitfalls of technology in education.
Java SE 8 Associate
The Java SE 8 course is designed to provide preparation for the Oracle Certified Associate (OCA) exam. Throughout the course, students will learn about Java from the basics to string builder methods. They will spend a significant portion of the course learning about the basics of Java, data types, operators, arrays, loop constructs, encapsulation, inheritance, exceptions, and API.
LEED Green Associate
This course introduces students to the LEED process. LEED, or Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design, is the global standard for green building certification. Throughout the course, students will gain an understanding of the various components of green building. The theme of sustainability and sustainable construction is woven throughout each module both in terms of physical environment and as it pertains to LEED certification. Additionally, this course prepares student for the LEED Green Certified Associate certification exam.
Personal Finance
The Personal Finance course is intended to prepare students to be successful financial citizens. They will learn their role and responsibilities as a responsible financial planner and saver as well as learn about the services, functions, and products of the financial industry. In addition, they will make informed buying decisions and understand personal taxation, wills, insurance, and contracts. Finally, they will learn about saving and investing as well as consumer credit and loans.
Principles of Architecture
In Principles of Architecture, students will review various concepts used in the design and architecture field. They will learn about basic drafting equipment and how to use and maintain it. They will analyze challenges and solutions within the development of design. They will also learn how to prepare drawings manually and using AutoCAD software. A substantial portion of the course will be spent on sequential processes so that students develop an understanding of creating and annotating drawings as well as how to apply standard rules regarding line types, offset objects, creating layers, and setting up a page for plotting. They will also explore three-dimensional drawing and use coordinating and navigation systems to create them.
Project Management
The Project Management course is intended to identify the key components of a career as a project manager. Students will review the basics in project management terminology, such as designating distinctions among projects, products, programs, and portfolios. They will delve into concepts like managing deliverables and creating engaging relationships with stakeholders. The primary components of project planning will be laid out and described in detail. Students will explore teams and organizational structures. They will discover project management tools and innovation being used in the industry. Overall, they will develop a greater understanding of the mechanisms that are in place to effectively carry out projects of any size through specific project management techniques.
Robotics: Applications and Careers
It seems like many elementary to high school robotics courses are focused on coding a simple robot to move its mechanical arm up and down. This course, in contrast, teaches students what a robot is and how it relates to other key technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning. Then the course examines 10 applications of robots and how they will change and impact various aspects of our lives and the economy. Will robots simply steal our jobs, or will they be a tool that will create new opportunities and even free humans to use our creativity and curiosity to their full potential? Students will grapple with this and many other questions as they explore this vital, future-focused subject.
A software development expert who can work on both the server and client sides of digital products is known as a mobile full stack developer. These technical experts typically work on a software program’s complete stack, which includes the front and back ends, the server, the database, the API, and more. We refer to these specialists as “full stack,” meaning they can perform nearly every position in the software development process because they utilize a wide variety of tech stacks tied to every aspect of app development.
Full-stack mobile development is when engineers who provide full-stack services can translate clients’ requests into the entire architecture or new technologies and implement them.
A full-stack developer need not be an authority in every technology, though. Such an expert must understand what is happening on both the client and server sides while building an application. They must be truly curious about and knowledgeable about every facet of full-stack mobile development.
In order to create a polished application, a full-stack mobile app developer must be knowledgeable about all stages of the development of digital products. They must be able to anticipate future problems and have a thorough awareness of how everything works from top to bottom. We will now go into greater detail about the difficulties that full-stack mobile development typically faces.
Full-Stack Mobile Development Market State
Full-stack development is on trend.The trend of employing a mobile full-stack developer first appeared a few years ago and is continuously growing. According to Indeed, the top three high-ranking careers in 2019 include full-stack developers. According to a CareerFoundry report on almost 26,000 open full stack opportunities in the US alone in 2022, there is a considerable need for mobile full stack engineers. This shift was brought about by a growing unification trend that contends comprehensive solutions are essential for growing businesses.
Requirements and skills
- Proven work experience as a Mobile developer
- Demonstrable portfolio of released applications on the App store or the Android market
- In-depth knowledge of at least one programming language like Swift and Java
- Experience with third-party libraries and APIs
- Familiarity with OOP design principles
- Excellent analytical skills with a good problem-solving attitude
- Ability to perform in a team environment
Full-Stack SDET
What is a Software Development Engineer in Test?
SDETs are in charge of ensuring that a product meets quality requirements before deployment. They accomplish this by monitoring each step of the product development process and making adjustments that range from the product’s most basic specifications to feature improvements and optimizations.
What do Software Development Engineers in Test do?
SDETs inspect and debug a product’s software to ensure it meets quality requirements throughout the development process.
Software Development Engineer in Test Responsibilities
- Establish broad and detailed quality standards for products.
- Make software tests that are both human and automated to find functionality problems.
- Examine the test results, then apply or tell developers about your solutions.
- Before a product is made available for purchase, check its functionality.
Day-to-Day Responsibilities of a Software Development Engineer in Test
- Create test scripts and cases to detect and fix coding errors.
- Keep track of quality issues and documentation.
- Repeat and confirm testing for earlier problems.
- Identify places where testing procedures need improvement.
Software Development Engineers in Test within a Company
SDETs are usually part of a product team and tend to report to senior QA engineers within a company.
Importance of Software Development Engineers in Test
SDETs proactively look for and eliminate product flaws that would otherwise go undetected during development. Their work enhances the usability of a product as a whole and its acceptance by customers.
Qualifications to be a Software Development Engineer in Test
- Two years’ worth of experience in software testing, development, or related fields.
- The capacity to create and carry out both human and automated software testing procedures.
- The capacity to analyze tests and confirm quality standards.
- Knowledge of software testing in relation to particular product development stages.
Software Development Engineer in Test Hard Skills
- Knowledge of A/B testing tools and software testing.
- Proficiency with programming languages for computers such as C#, Java, JavaScript, and Python.
- Knowledge of software debugging instruments.
- Familiarity with IDE programs, or integrated development environments.
- Understanding QA testing for console, mobile, and desktop platforms
- Software Development Engineer in Test Soft Skills
- Ability to pay close attention to detail.
- Critical thinking.
- Problem-solving skills.
- Verbal and written communication skills.
Software Development Engineer in Test Education and Experience
A bachelor’s degree in computer science, engineering, or a related profession is optional for SDETs. Even though many SDETs lack an IT background, they picked up the necessary skills through bootcamps.
Candidates for SDETs should have previous experience in roles related to software development, software testing, or other related fields. With the aid of internal initiatives, bootcamps offer this experience. It is advised to have some familiarity with product development, quality assurance, testing analysis tools, manual and automated software testing, and related tools and processes.
Software Development Engineer in Test Salary and Job Outlook
By 2031, employment in SDET roles will rise by 25%.
The complete compensation package for a SDET is based on a number of variables, including the candidate’s experience and location, among others
Bootcamp Curriculum
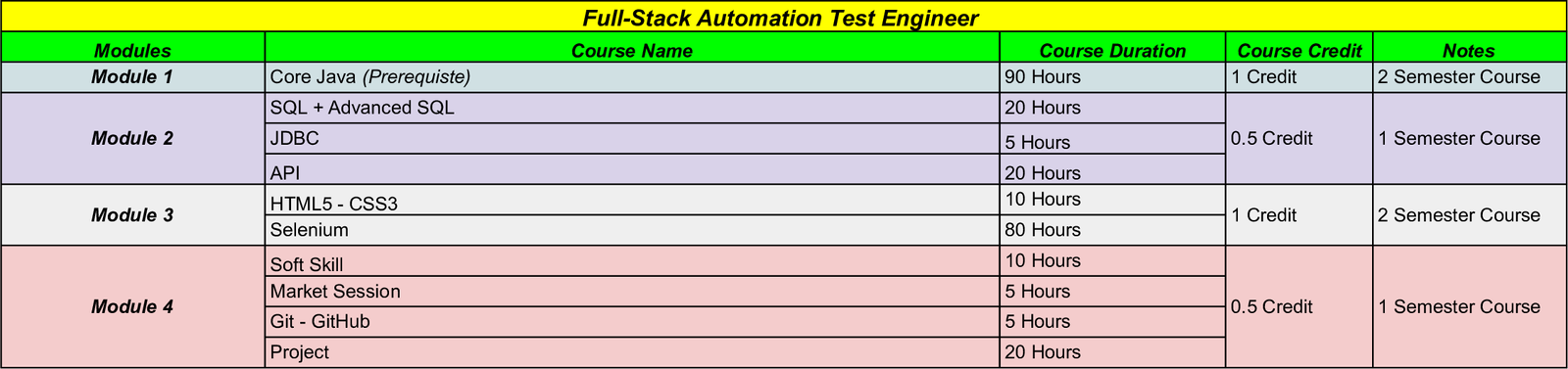
Full-Stack Java Developer
What is a Full-Stack Java Developer?
Web developers may choose to focus on back-end programming, front-end programming, or both. Full-stack programming is the practice of a web developer who is proficient in both front-end and back-end programming.
A developer who is skilled in both front-end and back-end development as well as the Java programming language and technology is known as a Java full-stack programmer.
What does a Full-Stack Java Developer Do?
In the Java coding language, a full-stack Java developer is in charge of creating the front-end components of software or websites as well as the back-end code and software systems.
Teams that produce software, websites, or applications are frequently led by full-stack Java engineers. Sometimes they work on these things by themselves.
What Is the Difference Between Java and Java Full-Stack?
Web developers who utilize Java to create the entire technology are referred to as Java full-stack developers.
This indicates that they utilize Java for back-end development and Javascript for the front-end.
The process of developing a website involves numerous steps, each of which requires a variety of tools. You must learn and master every Java full-stack technology to become a Java developer.
Is Java Full-Stack in Demand?
- The quick response is “yes”! The demand for Java full-stack engineers is high.
- Developers who are skilled in both front-end and back-end coding, building, and design are needed by tech corporations and website development firms.
- Today’s tech business is expanding quickly, and developers are in high demand. It is not anticipated that this will slow down.
How to Learn Java Full-Stack Development
- You’ve come to the right place if you’ve made the decision to study full-stack Java web development.
- Enroll in the web development bootcamp at Coding Dojo to learn more about Java full-stack and other topics.
- Simply select an online program, either full-time or part-time, accelerated or flexible. To provide you with more information, we offer online information sessions, a ton of materials, and a complimentary course bundle.
Is Java Full-Stack Easy to Learn?
- It takes time and effort to become a full-stack Java developer, and the route might be difficult.
- The Java and Javascript coding languages must first be mastered. After that, you must master every aspect of front-end and back-end development.
- You also need to study more coding languages, frameworks, other applications like Git and GitHub, site architecture, and how databases work in order to be well-rounded.
- Careers in full-stack web development are tough for the weak of heart, but the reward may be worth the effort.
Bootcamp Curriculum
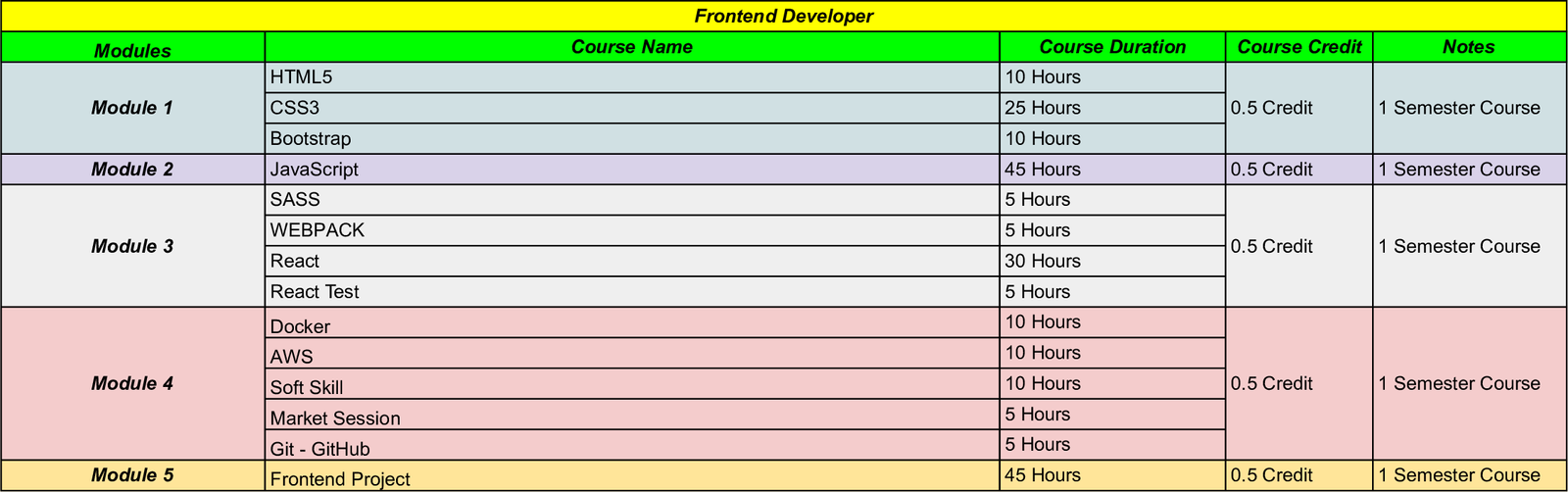
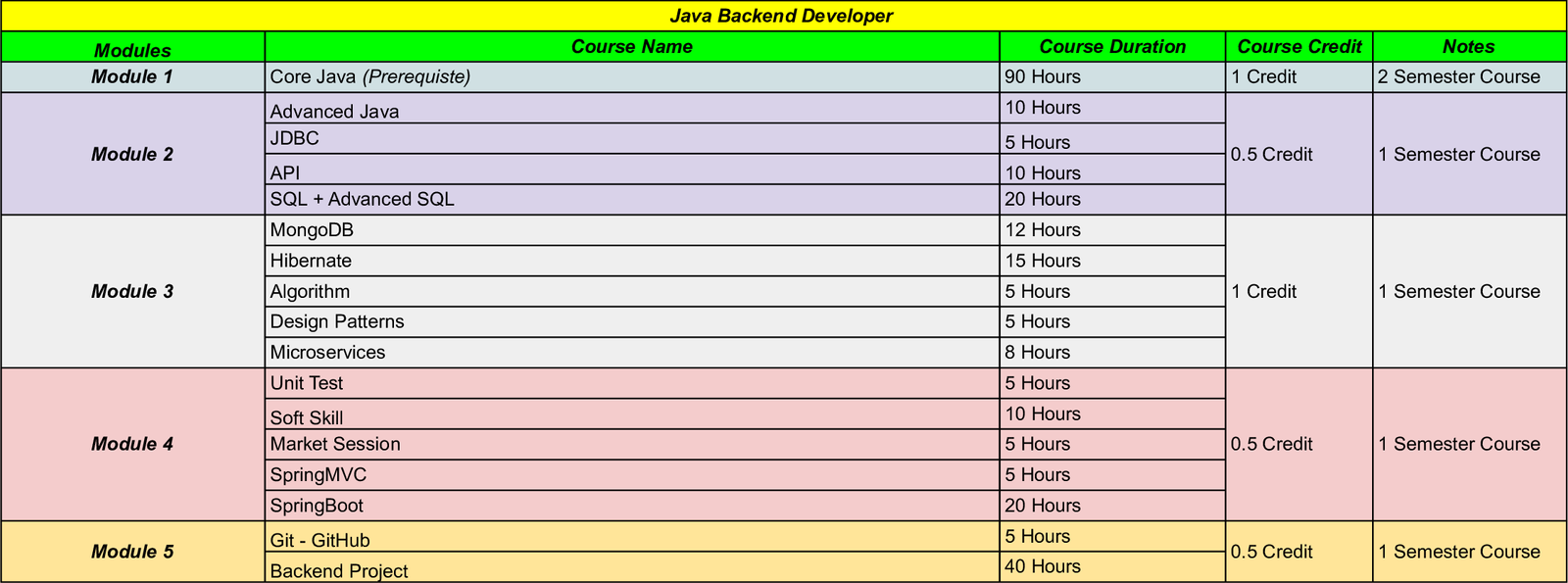
Front End Developer
What does a front end developer do?
Using web languages like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and React, a front-end developer develops websites and applications that people can access and utilize. The visual components of a website that you see were made by a front-end developer.
User interfaces (UIs) are made by front-end developers. The user interface (UI) of an application determines the function and visual appearance of each component of a website or application.
A front-end developer would design the site’s layout if someone wanted to establish a website. The front-end developer decides how to present the site, where to put images, and how the navigation should look. A large portion of their work includes making sure the design and organization of the website or application are user-friendly and intuitive.
Front end developer salary and job outlook
According to Glassdoor, front-end engineers in the US make an average salary of $84,235 a year as of February 2023. This sum includes a reported additional $5,719 in compensation on top of the average annual salary of $78,516. Profit-sharing, commissions, and bonuses are a few additional compensation insights that are possible. Salary ranges may be influenced by elements like experience, education, and certifications.
It is anticipated that demand for front-end development professionals will remain high for years to come. According to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), job growth for web developers is expected to be 23% between 2021 and 2031, significantly higher than the overall average of 8%.
How do front end developers work?
This role has several career options across numerous sectors and locales because of its demand and flexibility. You should be able to find a position that suits your interests, whether it be working for a non-profit, starting your own freelance firm, or working as an in-house developer for an organization.
There are many options for working remotely because the position involves a lot of computer use. Being a front-end developer may allow you to work from home for businesses located all over the country or even the world.
Workplace skills
You may be a better candidate to become a front-end developer if you possess particular non-technical (or soft) abilities in addition to knowledge of the technology that powers websites. You’ll want to have the following in mind:
- Creativity
- Problem-solving skills
- Written and verbal communication skills
- Teamwork
Bootcamp Curriculum

Back End Developer
What is back-end development?
Working on server-side software, or what you can’t see on a website, is what back-end development entails. By concentrating on databases, back-end logic, application programming interfaces (APIs), architecture, and servers, back-end developers make sure the website functions properly. They employ programming that facilitates database communication, data storage, comprehension, and deletion for browsers.
To create the framework of a website or mobile app, back-end developers work in tandem with front-end developers, product managers, primary architects, and website testers. Back-end engineers need to be knowledgeable about a wide range of frameworks and tools, including Python, Java, and Ruby. They guarantee that the back end responds promptly and effectively to user queries on the front end.
Back-end Developer Tasks and Responsibilities
Back-end developers need to be very skilled at collaboration as well as possess technical knowledge. You should have the independence to create the web infrastructure as a back-end web developer.
Many back-end developers work on the following projects on a daily basis:
Create and maintain websites: A back-end developer’s primary duty is to employ a variety of tools, frameworks, and languages to identify the most effective way to create and manage websites. Understanding cross-platform functionality and compatibility is necessary for this.
Write high-quality code: Web developers need to produce high-quality code in order to create long-lasting web apps.
Perform quality assurance (QA) testing:
To ensure optimal display across a variety of browsers and devices. Create and manage testing schedules to improve the user interface and experience. Testing for quality assurance (QA) is what this is.
Assess efficiency and speed:
When a website is launched, as well as throughout updates and alterations, developers must assess the website’s speed and scalability and make any necessary code improvements.
Troubleshoot and debug:
Be able to communicate problems to project managers, stakeholders, and QA teams while troubleshooting and resolving them.
Train and support:
You’ll be in charge of instructing and mentoring young developers, and keeping up with client teams’ practices will ensure continuing assistance.
Back-end developer salary and job outlook
According to Glassdoor, the anticipated median base salary for a back-end web developer in the US as of October 2022 is $82,462. According to Indeed, the average base salary is $95,472. Depending on your location, your level of seniority, and other elements, this may differ.
The demand for back-end developers is enormous. The US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects that the employment of web developers will increase by 23 percent between 2021 and 2031.
Back-end developer workplace skills
- These workplace abilities can help you collaborate more successfully, efficiently, and seamlessly with team members, in addition to your technical skills.
- Communication: In order to carry out the engineer’s vision, a back-end web developer must fully comprehend it. You can share any ideas and troubleshoot with team members and stakeholders with the aid of strong written and verbal communication skills.
- Problem-solving and analytical thinking: When creating a web or mobile app, you’ll need to think outside the box to solve problems like debugging and revising code without crashing the whole thing. As a developer, you should be able to identify the causes of a piece of code’s success or failure as well as foresee and eliminate problems.
- Industry knowledge: It’s always helpful to have a comprehensive understanding of the tech sector to stay on top of broader economic developments as well as changes to languages and platforms. Look into online and app development-related blogs, forums, news, and books to brush up.
Bootcamp Curriculum

Full-Stack Mobile Developer
What is a full-stack mobile app developer?
A software development expert who can work on both the server and client sides of digital products is known as a mobile full stack developer. These technical experts typically work on a software program’s complete stack, which includes the front and back ends, the server, the database, the API, and more. We refer to these specialists as “full stack,” meaning they can perform nearly every position in the software development process because they utilize a wide variety of tech stacks tied to every aspect of app development.
Full-stack mobile development is when engineers who provide full-stack services can translate clients’ requests into the entire architecture or new technologies and implement them.
A full-stack developer need not be an authority in every technology, though. Such an expert must understand what is happening on both the client and server sides while building an application. They must be truly curious about and knowledgeable about every facet of full-stack mobile development.
In order to create a polished application, a full-stack mobile app developer must be knowledgeable about all stages of the development of digital products. They must be able to anticipate future problems and have a thorough awareness of how everything works from top to bottom. We will now go into greater detail about the difficulties that full-stack mobile development typically faces.
Full-Stack Mobile Development Market State
Full-stack development is on trend.The trend of employing a mobile full-stack developer first appeared a few years ago and is continuously growing. According to Indeed, the top three high-ranking careers in 2019 include full-stack developers. According to a CareerFoundry report on almost 26,000 open full stack opportunities in the US alone in 2022, there is a considerable need for mobile full stack engineers. This shift was brought about by a growing unification trend that contends comprehensive solutions are essential for growing businesses.
Requirements and skills
- Proven work experience as a Mobile developer
- Demonstrable portfolio of released applications on the App store or the Android market
- In-depth knowledge of at least one programming language like Swift and Java
- Experience with third-party libraries and APIs
- Familiarity with OOP design principles
- Excellent analytical skills with a good problem-solving attitude
- Ability to perform in a team environment
Salesforce Administrator
What is a full-stack mobile app developer?
A software development expert who can work on both the server and client sides of digital products is known as a mobile full stack developer. These technical experts typically work on a software program’s complete stack, which includes the front and back ends, the server, the database, the API, and more. We refer to these specialists as “full stack,” meaning they can perform nearly every position in the software development process because they utilize a wide variety of tech stacks tied to every aspect of app development.
Full-stack mobile development is when engineers who provide full-stack services can translate clients’ requests into the entire architecture or new technologies and implement them.
A full-stack developer need not be an authority in every technology, though. Such an expert must understand what is happening on both the client and server sides while building an application. They must be truly curious about and knowledgeable about every facet of full-stack mobile development.
In order to create a polished application, a full-stack mobile app developer must be knowledgeable about all stages of the development of digital products. They must be able to anticipate future problems and have a thorough awareness of how everything works from top to bottom. We will now go into greater detail about the difficulties that full-stack mobile development typically faces.
Full-Stack Mobile Development Market State
Full-stack development is on trend.The trend of employing a mobile full-stack developer first appeared a few years ago and is continuously growing. According to Indeed, the top three high-ranking careers in 2019 include full-stack developers. According to a CareerFoundry report on almost 26,000 open full stack opportunities in the US alone in 2022, there is a considerable need for mobile full stack engineers. This shift was brought about by a growing unification trend that contends comprehensive solutions are essential for growing businesses.
Requirements and skills
- Proven work experience as a Mobile developer
- Demonstrable portfolio of released applications on the App store or the Android market
- In-depth knowledge of at least one programming language like Swift and Java
- Experience with third-party libraries and APIs
- Familiarity with OOP design principles
- Excellent analytical skills with a good problem-solving attitude
- Ability to perform in a team environment
Bootcamp Curriculum
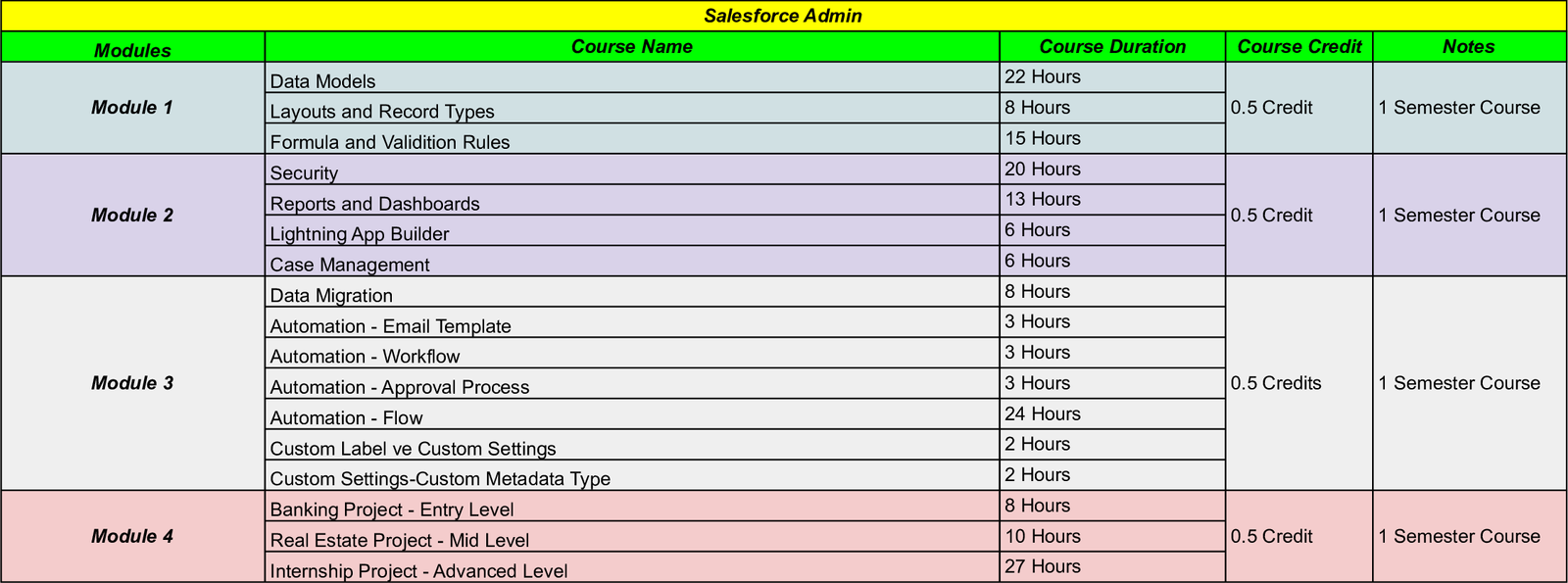
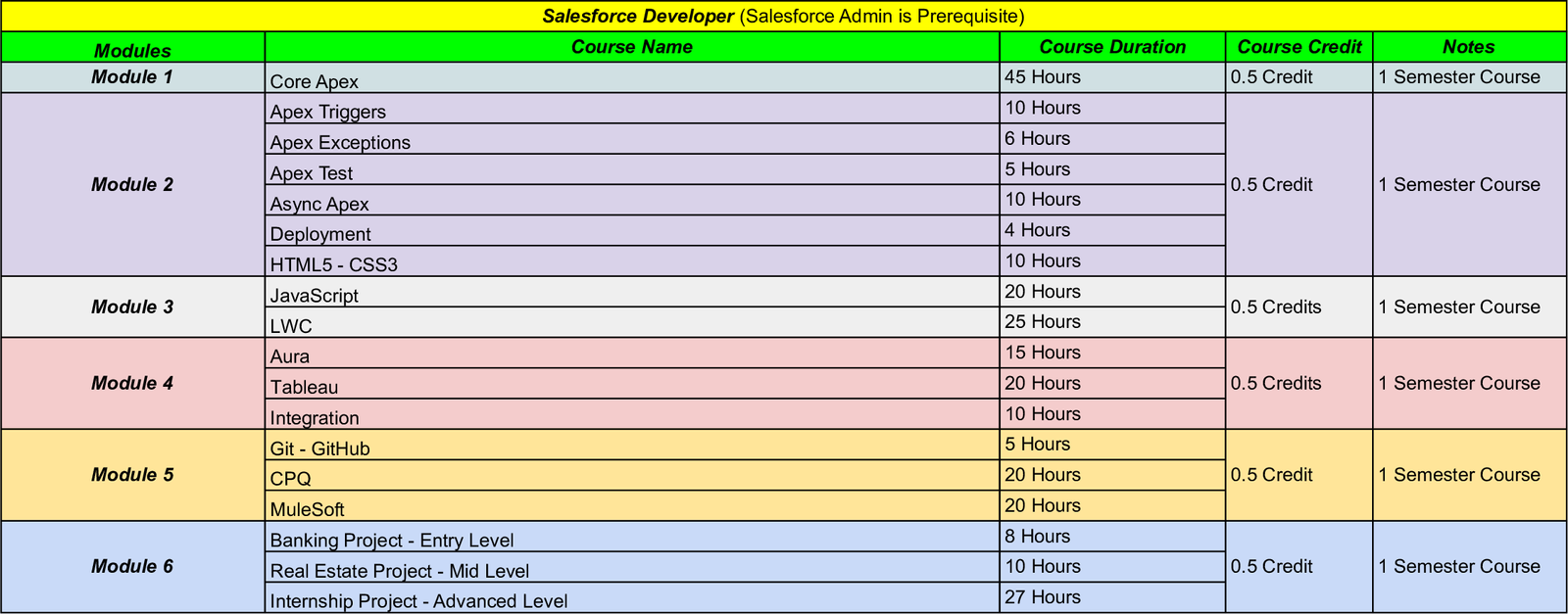
Salesforce Developer
What does a Salesforce Developer do?
The majority of Salesforce technology developers create unique company apps and solutions. They either use Heroku or the Salesforce Platform, which includes the communities for Sales Cloud, Service Cloud, and Experience Cloud. While some programmers specialize, the majority fall under the category of full-stack programmers, who work on both front-end user interfaces and back-end logic.
In the world of Salesforce, there are numerous options for developers outside of the Salesforce Platform. On Marketing Cloud, some people create unique marketing experiences. Others use Tableau to explore the depths of data and reveal fresh insights. With Commerce Cloud’s PWA kit, developers are creating interesting commerce experiences. Others use customized Slack apps to create their company’s digital headquarters.
Salesforce technologies offer opportunities for developers to work with every aspect of business applications.
Which skills does a developer need to work with Salesforce?
Every developer uses code, so you might be wondering what programming languages you could utilize. Quite a bit depends on the Salesforce area you choose to work in.
JavaScript and Apex are the two most well-known languages in the Salesforce community. Naturally, the language utilized for front-end changes as exposed by Lightning Web Components is JavaScript. The Salesforce ecosystem’s most extensively used back-end language is Apex.
However, we constantly broaden the range of languages that developers can utilize with Salesforce. Our functions-as-a-service (FaaS) offering, Salesforce Functions, was just released and currently supports JavaScript and Java, with Python on the horizon.
There are two domain-specific query languages available on the Salesforce Platform. A query language similar to SQL called Salesforce Object Query Language (SOQL) is used to access data in the Salesforce multi-tenant database. The platform’s text-based search language, Salesforce Object Search Language (SOSL), can be used to locate both data and documents that are stored there.
Some products support additional languages in addition to the Salesforce Platform. The Slack Bolt SDK offers compatibility for JavaScript and Python. You may use AMPscript for Marketing Cloud to create individualized marketing experiences. Your data transformations can be created in DataWeave if you create integrations with MuleSoft. If you deal with dashboards in Salesforce CRM Analytics, you might adjust visualizations using the Salesforce Analytics Query Language (SAQL). And most recently, the Customer Data Platform (CDP) has introduced SQL as a means of accessing its data.
The language and technological landscape for Salesforce are extensive and varied. Whatever your interests, there is a niche you can master.
Every developer working within the Salesforce ecosystem will eventually learn how to use the no-code tools that assist their job since Salesforce enables no-code customizations. As an illustration, simple user interface (UI) changes, data security rules, and wizards are all elements that can be implemented without any coding at all.
The simplest transition to working in the Salesforce industry is typically made by developers with prior experience in corporate software. But it’s not necessary in any way. I’ll say it again: Any developer can work at Salesforce. Many people transferred over from other software engineering positions or joined straight out of college.
Salesforce Developer salary and job outlook
Developers are still in great demand as the Salesforce ecosystem expands. The average annual growth in new developer roles over the last five years has been 206 percent. Additionally, a developer’s starting salary in the United States is $108,000 annually.
Salesforce is frequently chosen by developers looking for a job. Many people who come here become addicted to the helpful support of the Salesforce Developer Community. Local in-person meetups are another way to make connections, exchange ideas, and advance your career.
Through the Salesforce Developers group in the Trailblazer Community on Trailhead-Salesforce’s free online learning platform-participate in daily virtual conversations with developers.
Bootcamp Curriculum
Salesforce SDET
What is Salesforce Test Automation?
Writing scripts to run against your code and check whether various components of your application function as intended is the norm for automated testing.
Software is used to generate and execute automated tests. They ultimately enable enterprises to achieve a high level of quality by assisting in the detection of issues before they affect end customers.
Salesforce test automation is a type of automated testing specifically designed to address the highly complicated nature of all the various components that make up a Salesforce application.
Importance of Salesforce Test Automation:
Salesforce Test Automation is able to find flaws in custom code as well as in Salesforce apps.
Automate monotonous chores so you don’t have to use up valuable time or staff.
Limit manual testing to only those circumstances when it is required to reduce human error and expenditures.
Salesforce Test Automation ensures that the feature used today is functioning as intended.
Salesforce test automation aids in testing the application during both its development and deployment phases.
Benefits of Salesforce Test Automation
Increased Test Coverage:
Automated testing allows you to run hundreds of tests. These will enable you to thoroughly cover all possible eventualities. The majority of your application must be tested in order to ensure that it can successfully react to Salesforce’s regular upgrades.
Enhanced Accuracy:
Hours of manual testing are a tiresome chore that can easily result in errors. By using automated testing, you can eliminate the human element. This ensures that every test case is run continuously and accurately.
Early Problem Detection:
Test automation will assist you in finding issues with your Salesforce instance before they worsen and start to have an impact on your company.
Money and Time Savings:
Testing a Salesforce application by hand is an expensive and time-consuming task. At a fraction of the cost and time, the bulk of the same tests can be automated. By identifying issues sooner and preventing them from occurring in production, Salesforce test automation will enable you to save money. You can also use the time that has been freed up for other worthwhile pursuits. Additionally, you can save money by using the same automation scripts for a variety of test cases.
Gaining Valuable Insights:
Automated testing also allows for the automatic generation of reports. These give you useful information about how well your Salesforce application components are performing. You can modify your testing strategy and concentrate your efforts where you detect potential issues or where you feel vital based on the findings of your tests.
Which automation tool is the best for Salesforce Testing?
Additionally, they inquire about the ideal automation tool for Salesforce testing. Salesforce is a pretty complicated platform with numerous distinctive features, as was already noted. Flexibility and strong capabilities are needed in an automated solution to test Salesforce thoroughly and effectively.
Selenium is a well-liked tool that supports a wide range of programming languages and can conduct automated tests on many web browsers and systems. Selenium can be used for Salesforce testing; however, it’s not the most effective solution. To write tests, you must have extensive coding abilities, and it frequently fails due to shadow DOM issues.
Bootcamp Curriculum

Cyber Security Analyst
What is a Cyber Security Analyst?
The main duty of a cyber security analyst is to defend a company’s systems and network from online threats. This includes looking into impending IT trends, developing backup plans, analyzing suspicious activity, disclosing security breaches, and training the rest of the organization on security precautions.
Implementing security controls and threat protection measures is another duty of cyber security analysts. To identify any potential weaknesses that might exist within the organization, they might even simulate security attacks.
Cyber security experts must keep up with the numerous advancements in hackers’ digital weapons since they are always utilizing new tactics and technologies.
Cyber Security Analyst Job Description
Cybersecurity experts are increasingly in demand as cyberattacks and threats increase in frequency. A startling 7.9 billion records were exposed by data breaches in the first nine months of 2019, according to Risk-Based Security. There were 112% more records exposed in 2018 as a result of this.
Jobs for cyber security analysts are expected to increase by up to 31% between 2019 and 2029, which is substantially faster than the average for all occupations. For various companies and industries, a cyber security analyst’s job description may vary. But the following characteristics are shared by all of them:
- Set up antivirus programs and consoles, and handle routine tasks and data structures.
- Analyze threats and risks, then offer workable solutions.
- Data gathering and analysis to address risk, performance, and capacity challenges
- Making tools and participating actively in security architecture reviews
- Create and implement security features and protocols.
- Install and integrate security software programs.
- Create security standards and improve new technology services.
What Are Cyber Security Analyst Roles and Responsibilities?
An analyst for cyber security gets ready for and handles cyberattacks. Although this procedure may vary among workplaces, businesses, and industries, the basic premise is the same. Here are some typical functions and duties for a cyber security analyst:
Manage Software
All systems and networks in a business should have software installed, managed, and updated, as well as proper security measures.
Monitor Networks
Keep track of network traffic by monitoring it, spotting malicious behavior in incoming code, and taking appropriate action
Develop Security Plans
Advising staff members and end users on good data security practices.
Reporting
Compile regular safety reports and keep track of security problems and the steps taken to fix them.
Research
Study up-and-coming information technology and security trends, keep abreast of prospective dangers and attacks, and develop preventive measures.
Certifications Required to Become a Cyber Security Analyst
Certified Ethical Hacker Certification
With a Certified Ethical Hacker certification, you can ethically apply your understanding of hacking to enhance an organization’s security. This certification proves that you possess the abilities to scan target systems for flaws and vulnerabilities like a malevolent hacker would, but you do so in a legal and proper way to evaluate the security of businesses.
CISSP Certification
The International Information Systems Security Certification Consortium (ISC) developed the Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) certification, which is a widely recognized information security credential. It certifies your proficiency using internationally recognized information security standards in creating, constructing, and maintaining a secure company environment.
CISA Certification
The Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA) grants the title of “Certified Information Systems Auditor,” or “CISA Certification.” This internationally recognized credential attests to your proficiency in information system auditing, control, and security.
Cyber Security Analyst salary and job outlook
A cyber security analyst’s pay is influenced by a number of variables, including experience, education, skills, industries, and geographic areas. The US Bureau of Labor Statistics estimates that a cyber security analyst makes an average salary of $99,730. The top 10 percent of earners earn more than $158,860 annually, while the bottom 10 percent make around $57,810.
Bootcamp Curriculum

SQL Developer
What is a SQL developer?
A database specialist known as a SQL developer frequently collaborates with business analysts, database administrators, and other IT specialists. By building and maintaining databases, SQL developers assist businesses in managing and modifying their data.
SQL Developer Job Responsibilities
An SQL developer’s duties include planning, creating, and managing SQL databases in order to create and administer them. SQL developers utilize CRUD SQL commands to build and change database tables using structured query language (SQL). CRUD, which stands for create, read, update, and delete, refers to the four operations programmers use to modify data in database tables.
You’ll evaluate queries, build sophisticated functions and stored procedures, optimize database performance, design security measures, and fix issues as a SQL developer. They could develop dashboards, run intricate queries for business intelligence reporting, or design database architecture.
In an e-commerce database, a command to retrieve all records pertaining to a certain client is an example of a simple query and application capability. Enterprise resource planning (ERP) for supply chains is an example of a sophisticated piece of code that uses several tables linked by a web of interlinked links.
The code created by SQL developers enables users to interact with the data kept in databases, access metrics that provide important business insights, and enhance organizational decision-making.
Workplace Skills
You must have exceptional people skills if you want to work as a SQL developer. The ability to communicate with peers in IT roles and subject-matter experts is a must for SQL developers. They must also be able to communicate functional business requirements to experts who lack a strong technical background. On a daily basis, they might work with a variety of project professionals. This could take place in person or virtually.
SQL Developer Education and Experience
Like many other professions, becoming a SQL developer can be aided by a good educational foundation. For some jobs, a high school education might be sufficient, but many firms favor applicants with bachelor’s degrees in computer science, data analytics, data management, mathematics, engineering, statistics, or a closely related discipline.
For SQL developers, master’s degrees in these areas are helpful. Students acquire sophisticated programming techniques in these programs, which expand on undergraduate coursework and help them become more skilled SQL developers. Computer science, data analytics, and information technology are frequently the main areas of concentration in master’s degrees for SQL developers.
SQL Developer Salary and Job Outlook
The average SQL developer’s annual salary is $97,539, while the average annual salary for a senior SQL developer is $129,027
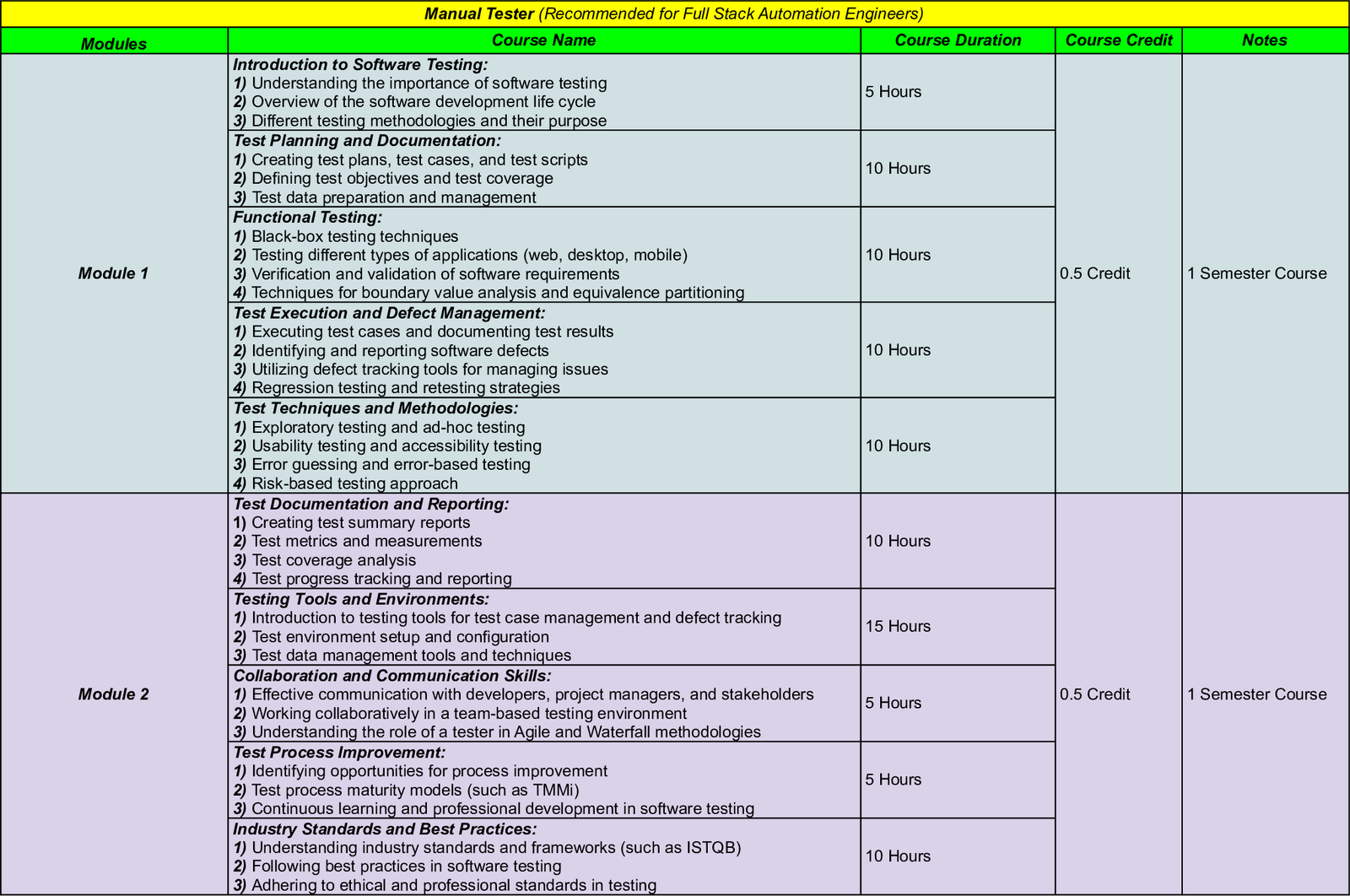
Manual Tester
What is a QA (Quality Assurance) Manual Tester?
Software is tested manually by QA personnel rather than automatically. Discover what a manual tester does in the next paragraphs, along with the needed qualifications and pay for QA manual testers.
Software testing must include quality assurance, which is essential. Without it, the digital world would be riddled with glitches and other issues. There are now two methods used for QA testing. The first is automated and carried out by computers, while the second is manual and carried out by people. Explore the QA manual tester’s job description and the route that leads to this crucial position by reading on.
What does a QA Manual Tester do?
A manual QA tester checks new software both before and after it is published for issues and faults. Your job is to point out problems and assist developers in finding solutions.
White box and black box testing are the two primary categories of QA manual testing. You are typically a member of the development team in a white box and are aware of what the code should do. You experience the software as a novice user would when in a black box.
As a manual QA tester, you might execute a wide range of test scenarios. On occasion, you’ll make sure the software works well with other programs or is adaptable to a variety of hardware.
How to become a QA Manual Tester
You must first and foremost comprehend the software development lifecycle (SDLC) to be successful as a manual QA tester. You will, after all, be an essential component of the SDLC.
Excellent analytical abilities and the capacity for efficient written and verbal communication with others are additional prerequisites for QA manual testers. Additionally, you need to be able to think creatively and solve problems. After all, the goal of QA manual testing is to identify potential issues, test for them, and then fix any that are discovered.
Each software developer has different criteria in mind. There are some businesses that need QA manual testers with a lot of experience. Others will be delighted to take on eager newcomers.
Why do companies need QA Manual Testers?
Developers will write test cases that outline step-by-step what must be done to verify that a feature is functional in order to test software. A mobile app developer might create a test case, for instance, to observe what happens if the user receives a call or text while utilizing the app. Since people have numerous other brand loyalties, they will also need to test this on many different kinds of devices.
Once a person creates the test case, some testing can be completed by test automation frameworks, along with additional tools and technologies. However, there are still some tasks that developers would want a manual QA tester to complete. Next, we’ll go into greater detail about the distinctions.
QA Manual Tester salary and job outlook
The outlook for QA manual testers and other roles in software development and QA is strong.
Employment in this area is projected to grow 25 percent from 2021 to 2031, much faster than the average for all occupations
Bootcamp Curriculum
Game Developer
What is a Game Developer?
Developers of video games aid in turning a game’s concept into a playable reality. To achieve this, they program functionality, code visual aspects, and test iterations until a game is ready for sale. A career in video game production can be extremely lucrative if you enjoy working with computers and video games. The creation of aesthetics, artificial intelligence, user interfaces, and game logic are all common responsibilities of game developers.
What are the tasks and responsibilities of a game developer?
Depending on the size of the firm you work for and your area of expertise, the job you do as a game developer will change. You’re more likely to have a more specialized function working on a particular aspect of the game at larger gaming businesses. You might participate in a variety of game lifecycle procedures at an independent publisher. Among the regular duties you might have in this position are some of the following:
- Create innovative game design concepts.
- Convert visual concepts into code.
- Gameplay prototypes should be refined over time.
- Work with producers, artists, and quality controllers.
- Track the platform-specific stability of games.
- Review the current code and suggest improvements.
- Transfer games or components between systems.
Game Developer Career
Many game creators enter the field because they enjoy playing video games. Video games are a popular type of entertainment in the United States, where more than 215 million people play them, according to the Entertainment Software Association. While working in the video game industry might be difficult, it can also be satisfying to contribute to the creation of something that both you and your potential customers are enthusiastic about.
Game Developer Salary and Job Outlook
According to the International Game Devs Association’s (IGDA) 2021 Developer Satisfaction Survey, 63 percent of fully employed devs reported making more than $50,000 annually. As of October 2022, the employment website Glassdoor estimates an even higher average base salary for game developers in the US of $74,832.
According to the IGDA, the video game industry has a history of rapid growth and will probably continue on that path. Jobs may become more available as gaming drives innovation in fields like artificial intelligence (AI), esports, virtual reality (VR), and augmented reality (AR).
Digital Artist
What is a Digital Artist?
Using a computer and modern software applications, digital artists can work on a range of projects, such as video animation, internet user interfaces, artwork for the visual components of a video game, illuminating a medical text, producing two-dimensional pictures for fashion design, and more.
Depending on the project, a digital artist may create a variety of digital assets, such as 3D characters and environments, storyboards, textures for artwork, animations, and 3D effects. Digital artists work alongside editors to produce visual effects for movies and television.
What does a Digital Artist do?
Graphic designers use color, images, typefaces, and layout to visually communicate a message or a product. They create logos, print materials, product packaging, websites, and more.
There are many different jobs and industries that graphic designers work in.
For example, a designer may work for a design firm with a variety of clients and projects, or they may be employed directly by a company to work on marketing materials. Many graphic designers also work as independent contractors for themselves, accepting contracts as they come up.
- 7 Careers in the Digital Arts
- Graphic/Digital Designer.
- Game Art and Animation Artist.
- Web Developer and Designer.
- Digital Videographer, Editor, and Producer.
- Art Director.
- Advertising, Promotions, and Marketing Manager.
- Director of Marketing to Chief Marketing Officer.
Digital Artist Salary and Job Outlook
Digital artists in the United States earn an estimated $52,744 in total compensation annually, with an average wage of $49,148. These figures show the median, or the midpoint of the ranges, from our unique Total Pay Estimate methodology, which is based on data about wages gathered from our users. The expected annual increase in wages is $3,597. Cash bonuses, commissions, tips, and profit sharing are all possible forms of additional compensation. The values in the “Most Likely Range” fall between the 25th and the 75th percentile of all the pay information that is currently available for this role.
VR Designer
What is a Virtual Reality Designer (VR)?
Companies today produce more than just goods and services. They also deal with how the object interacts with its surroundings and users, showing the benefits that the user might derive from the experience by giving it some significance. The development of virtual reality opens up a new area for investigation in this discipline.
The innovative ideas being researched in the sectors of aviation, automobiles, high-tech, luxury, banking services, healthcare, hospital systems, etc. are extremely complicated in terms of interaction, integration, or idea, and before they are put into practice, they must be conceptualized, thought of, produced, and virtually simulated.
For instance, building an autonomous car’s infrastructure will require building vehicle stations in cities, imagining not only how to use the vehicles but also how to use the city (passer-by recognition, interacting with other vehicles, etc.). The scenario to think about, construct, portray, and mimic in virtual reality will include all of this intricacy.
What are the tasks and responsibilities of a Virtual Reality Designer?
By utilizing all the options provided by the 3D tools, the virtual reality designer creates the user experience in a collaborative setting. Holograms, augmented reality, virtual reality, immersion…
While certain experiences will be integrated into our reality, others will remain in the virtual realm. The 3D offers simulation opportunities with scales, expenses, and perilous circumstances that are impossible to approach in the actual world: modeling of crowd flow, nanorobot surface behaviors, nuclear plant emergency systems, and flight simulators.
The virtual reality designer will be able to employ design principles to create the 3D products and services of the future, as well as the experiences of their use in simulated real-world settings, thanks to his perfect mastery of the 3D tools. But before beginning the construction of these 3D experiences, he will also demonstrate how to skew these tools in order to realize, prototype, and create them.

